
UX vs. UI: What are the Differences?
In digital design, two terms that often intermingle yet hold distinct roles and characteristics are UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface).
Many assume UX and UI are interchangeable terms, but understanding their distinctions is vital for knowing how to create impactful digital tools that resonate with users and drive success for developers and designers.
Think of It Like Going on a Road Trip
- Imagine going on a road trip. Here, the "UI" would be the vehicle you drive—the dashboard, the controls, and the navigation system you interact with. It needs to be well-designed and intuitive for a smooth ride.
- The UX, however, is the entire journey – the scenic routes, the comfort of the seats, the music playing, and the overall enjoyment of the trip.
- A perfect road trip requires a reliable and easy-to-use car (UI) and a pleasant and enjoyable journey (UX) that creates lasting, and hopefully happy, memories.
What is ‘UX’?

UX stands for “user experience” and encompasses a user's holistic website journey with a product or service, from initial interactions to post-interaction feedback.
As a discipline, UX goes deep into understanding user behaviors, motivations, pain points, and needs.
That’s why UX typically involves extensive user research, creating user personas, defining user flows or pathways, and conducting usability testing.
Goals and KPIs for UX
A well-crafted UX strategy aims to create positive, intuitive, and enjoyable experiences that effectively meet user needs and solve problems. It focuses on reducing friction, increasing user engagement, and driving desired actions, such as conversions or product adoption.
Key metrics for measuring UX success typically include user satisfaction scores (these may be either quantitative or qualitative, or both), task completion rates, adoption rates, and retention rates.
What is ‘UI’?
UI stands for “user interface” and focuses on a product or service's visual and interactive elements that users directly engage with.
UI designers work closely with UX strategists to translate user research, wireframes, and prototypes into visually appealing and functional interfaces that align with user goals and brand standards.
The final UI typically comprises typography, color schemes, layout, interactive components like buttons and menus, and overall visual design aesthetics.
Goals and KPIs for UI Design
Well-designed UI elements play a crucial role in enhancing the usability, accessibility, and appeal of digital interfaces.
The success of a UI will typically be measured by its visual appeal, the level of user engagement with interface elements, and how well the UI conforms to brand guidelines and industry best practices.
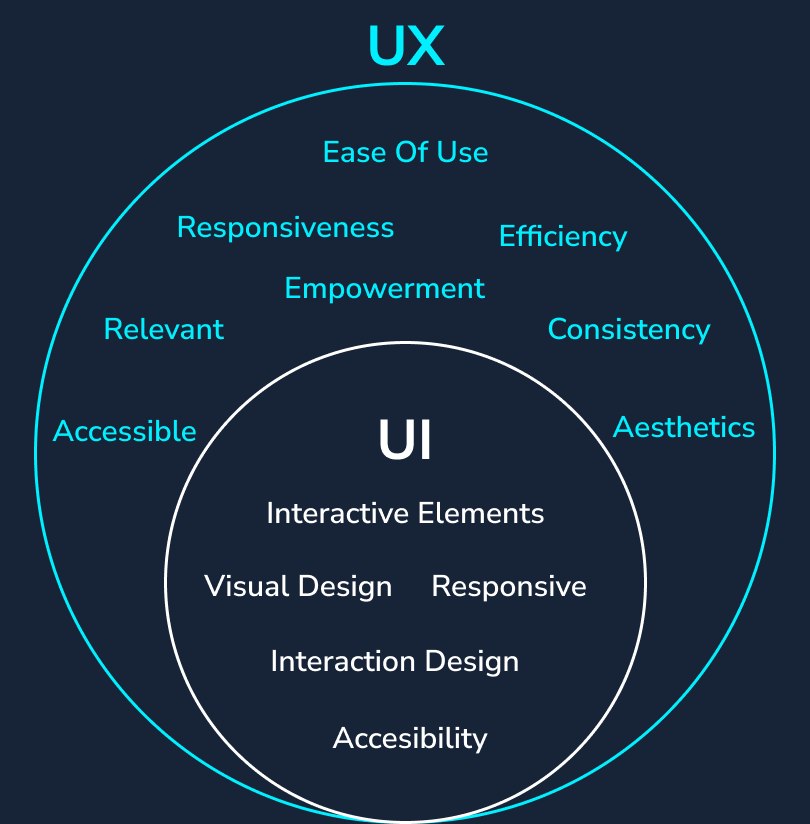
UX is about the overall experience, while UI is about the specific visual and interactive aspects.
Key Differences Between UX and UI
While both are integral for creating successful digital products, UX and UI serve distinct purposes and require different skill sets.
Let's explore the key differences between UX and UI to gain a deeper insight into their roles and contributions to digital experience design.
UX |
UI |
Focus and Scope |
|
| Encompassing the entire user journey and experience from start to finish. It considers not only the interaction with the product or service but also the pre-interaction research phase and post-interaction feedback loop. | Focuses specifically on the visual and interactive elements that users directly interact with on the screen. This includes designing layouts, aesthetics, and functionalities of buttons, menus, navigation elements, and other interactive components. |
Skill Sets and Responsibilities |
|
| Strategists analyze user data and feedback to iterate and improve the overall user experience.
Responsibilities
|
Designers create mockups, style guides, and design systems to ensure visual consistency and brand identity across the product. They focus on visual design aspects.
Responsibilities
|
Goals and Outcomes |
|
| The primary goal is to create intuitive, user-friendly experiences that resonate positively with the target audience. It focuses on reducing friction points, increasing user engagement, and driving desired actions. | Enhance the visual appeal and usability of digital interfaces. It emphasizes usability, accessibility, and consistency in design elements to improve user interaction and navigation. |
Timeline and Iteration |
|
| In the iterative digital design process, UX research and planning phases precede the UI design phase. Strategists conduct extensive research, develop user personas, define user flows, and create wireframes and prototypes. Once translated into functional UIs, these prototypes are subjected to rigorous usability testing, A/B testing, and analysis to gather insights for iteration and improvement. | Designers collaborate with UX teams to translate wireframes and prototypes into visually compelling and functional interfaces, ensuring that the visual design aligns with user experience goals and business objectives. |
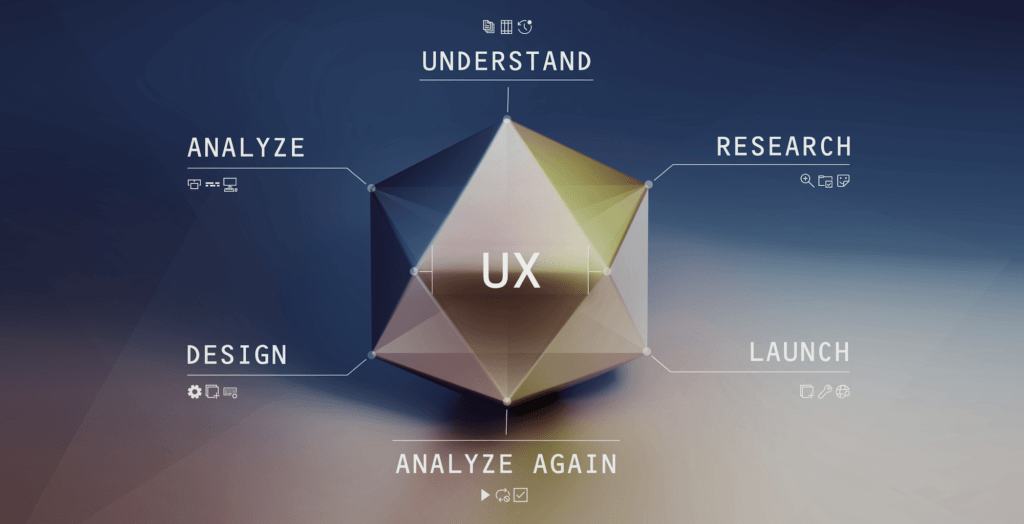
The Role of Developers
Developers play a crucial role in UX strategy and UI design processes, bridging the gap between a project’s scope, user goals, design concepts, and functional implementation.
Developers and UX Strategists
Developers collaborate closely with UX professionals to bring wireframes, prototypes, and user flows to life. They ensure the user experience design is translated into functional interfaces, implementing features that enhance usability and user interaction based on UX specifications. This involves coding functionalities, integrating APIs, and optimizing performance to create seamless user experiences.
Developers and UI Designers
In UI design, developers work hand-in-hand with UI designers to transform visual designs into interactive interfaces. They translate the visual elements of mockups into code, ensuring pixel-perfect accuracy and consistency across different devices, screen sizes, and platforms.
The Crucial Bridge Between UI and UX
Overall, developers are integral to both UX and UI design processes, turning design visions into tangible digital experiences that meet user needs and business objectives.
Once a product is launched, developers play a critical role in conducting A/B testing, optimizing UI elements for responsiveness and accessibility, and integrating analytics tools to measure user engagement and behavior. This allows designers and strategists to validate their assumptions and iterate products to continuously improve them for users.
UX research informs UI design decisions, and UI feedback also influences UX iterations, leading to a cohesive and user-centered design approach. Interdisciplinary teamwork and collaboration fosters creativity, innovation, and optimal user experiences.
Combining UX and UI for Your Digital Success
While UX and UI are interconnected and complementary, it’s important to understand how they serve distinct purposes. Knowing their differences and how they collaborate is essential for creating exceptional user experiences that resonate with users and achieve business objectives.
A great user experience often goes unnoticed. A poor user experience is unforgettable.
See how we create beautiful and functional UX. View Our Portfolio →
At DBS, we prioritize UX and UI to craft websites and apps that look visually appealing and function intuitively, ultimately leading to improved user satisfaction, engagement, and digital success.
FAQs
UX stands for User Experience, which focuses on designing websites with a human-centered approach. It requires an understanding of users’ needs, behaviors, and emotions to create digital experiences that are intuitive, enjoyable, and satisfying.
UI stands for User Interface, where humans interact with digital products, like websites and apps. The UI connects users with visual elements such as buttons, menus, and layouts, allowing them to navigate and engage with a website easily.
User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) are closely related yet distinct concepts. UX refers to the overall experience of using a website. It's focused on ensuring users find what they need without frustration and enjoy their time there. UI, in contrast, includes the visual design elements that users interact with, such as buttons, menus, navigation, and layouts. Together they incorporate the design thinking approach focused on human-centered design.
It helps to create websites visually appealing and user-friendly to improve user satisfaction and engagement.
Well-executed UX design reduces friction, increases user engagement, and drives actions like conversions.
The purpose of UI design is to create visually appealing website interfaces and accessible designs that offer intuitive navigation and visual appeal for a positive and pleasurable browsing experience.
The design of the User Interface (UI) focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a website or app, such as layout, colors, buttons, and menus to create an appealing and intuitive experience.
User Experience (UX) focuses on creating a smooth, intuitive, and enjoyable user experience by understanding their needs. A well-designed User Interface (UI) supports the user experience.